Elements
Table of Contents
The WPFilters Elements page provides all the essential tools you need to create flexible filtering options for your site’s content. This comprehensive interface allows you to build custom filter controls that enable visitors to narrow down and find specific posts, products, or custom post types based on various criteria.
Filter Fields
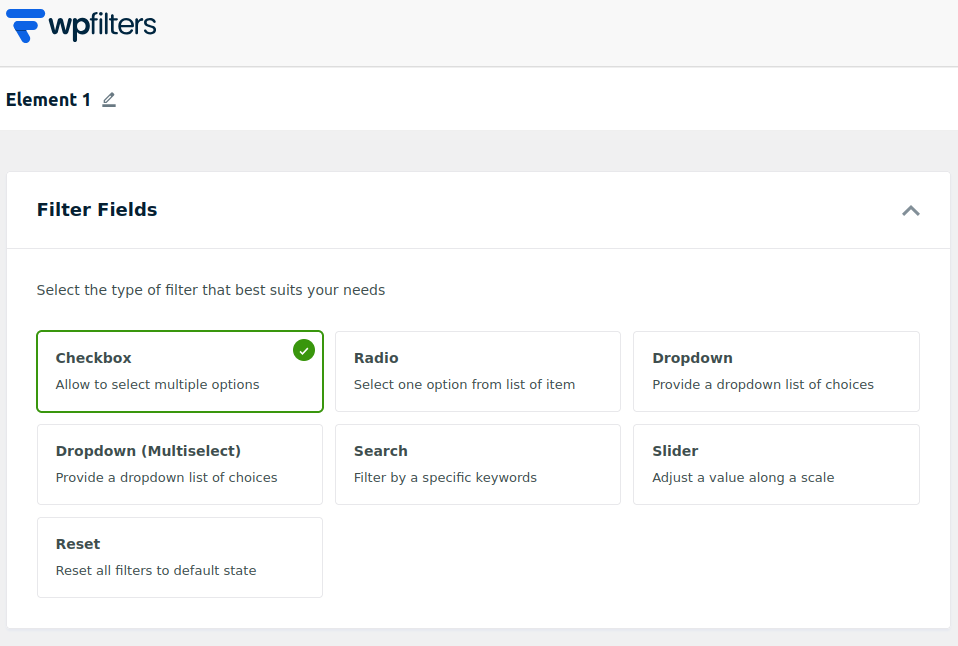
Filter Fields define what type of input control will be displayed to the user. Each field controls how users can select values to filter the content. WPFilters provides multiple field types suitable for different needs:
Checkboxes: Displays multiple selectable options. Users can check more than one value at the same time, making it useful for filtering by categories, tags, or any field with multiple possible selections.
Radio Buttons: Allow users to select only one option from the available list. Ideal when the filter requires a single, exclusive choice.
Dropdown: Displays all available filter options within a compact dropdown menu.
Dropdown (Multi-Select): Works like a standard dropdown but supports selecting more than one option. This is useful when you want a compact display but still allow multiple selections.
Search Bar: Allows users to filter content by text keywords. The search bar integrates automatically with WordPress’s native search functionality and also works seamlessly with SearchWP when the plugin is active.
Slider: Displays a visual slider input for selecting numeric ranges, such as price, size, quantity, or custom numerical values stored in custom fields.
Reset Button: Resets all applied filters and returns the results to their default unfiltered state.
Data Source
The Data Source determines where the filter retrieves its values from. WPFilters can automatically detect several different data types from your site:
Taxonomies: Use taxonomies such as WordPress categories, tags, or any custom taxonomy registered on your site. This includes WooCommerce product categories, product tags, and other custom taxonomies.
ACF Fields: If your site uses Advanced Custom Fields, WPFilters can automatically detect ACF text, select, number, and other supported field types. Selecting an ACF field will load and display all values stored in that field across your posts and pages.
Post Type: Allows users to filter content based on the post type, such as Posts, Pages, Products, or any custom post type.
Post Date: Filter posts by published or modified date. Useful for listing recent posts, archives, or news updates.
Post Title: Filters results based on the post title.
Post Author: Displays a list of site authors and allows filtering posts created by specific authors.
Container Settings
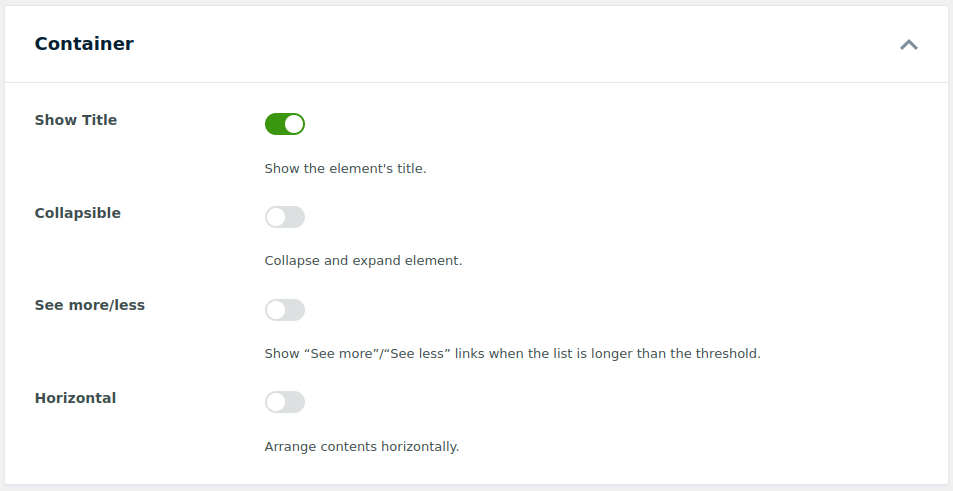
The Container section defines how the filter block itself appears on the front end:
Show Title: Toggle whether to display the element’s title above the filter controls, helping users understand what each filter represents.
Collapsible: Adds expand/collapse functionality to the filter block. This is useful for saving page space, especially on pages with many filter groups.
See more/less: Displays “See more”/“See less” links for checkbox filters when the number of items exceeds a specified threshold. When this option is enabled, an additional Show more after numeric field appears, allowing you to define how many items should be visible initially before the “See more” link appears.
Horizontal Layout: Displays filter items side-by-side instead of one per line. This is especially useful for checkboxes or radio options if you want a compact layout that fits more items on a single row.
Items Settings
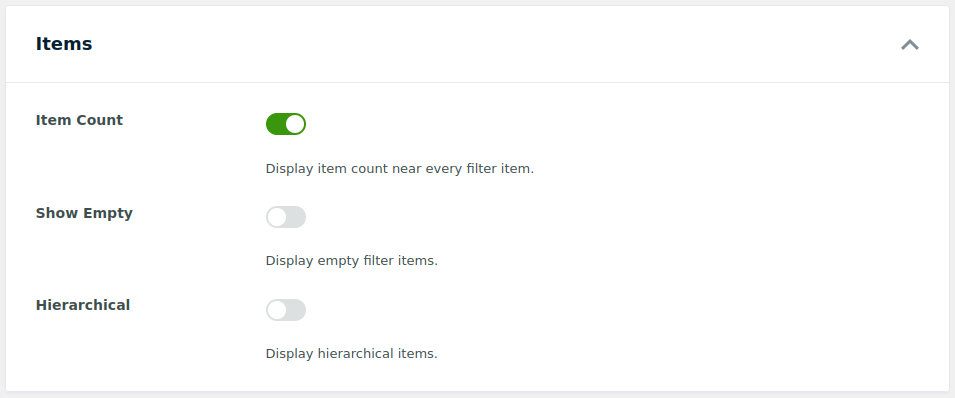
The Items section controls how the individual filter choices are presented:
Item Count: Display the number of available posts next to each filter option. For example, if using categories as a data source, enabling this option will show the total post count for each category value in your filter field.
Show Empty: Allows empty options to appear in the list even if no posts currently match that value. Disable this to hide terms or values that have zero matching items.
Hierarchical: Displays values in a parent–child structure. For example, a “Category > Subcategory” layout where nested items appear indented below their parent term.
Advanced
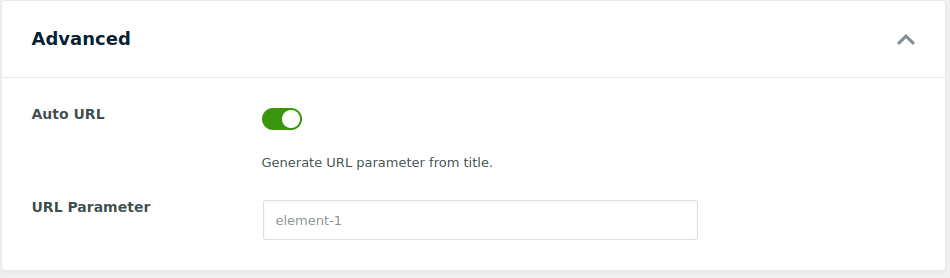
The Advanced section provides technical options for deeper customization:
Auto URL: This option is enabled by default, allowing WPFilters to automatically generate a URL parameter based on the element’s name. Disable this toggle if you want to manually define your own parameter name.
URL Parameter Name: When Auto URL is turned off, you can define a custom parameter name. This allows you to use a shorter or more meaningful parameter, improving URL readability and helping with integrations—such as tracking tools—or ensuring compatibility with custom URL structures.
Live Preview
The sidebar includes a live preview section that shows how your filter field and data values will appear on the frontend of your site. This real-time preview updates after you save your settings, allowing you to verify the appearance and functionality of your filters before publishing them to your live pages. The preview helps ensure that your filter controls match your site’s design and meet your usability requirements.
Embedding Filter Elements
Once you’ve configured your filter element settings, you’ll need to embed it on your pages. WPFilters provides multiple embedding options to accommodate different workflows and technical preferences. Click the “Embed” button next to the save settings option to access these embedding methods.
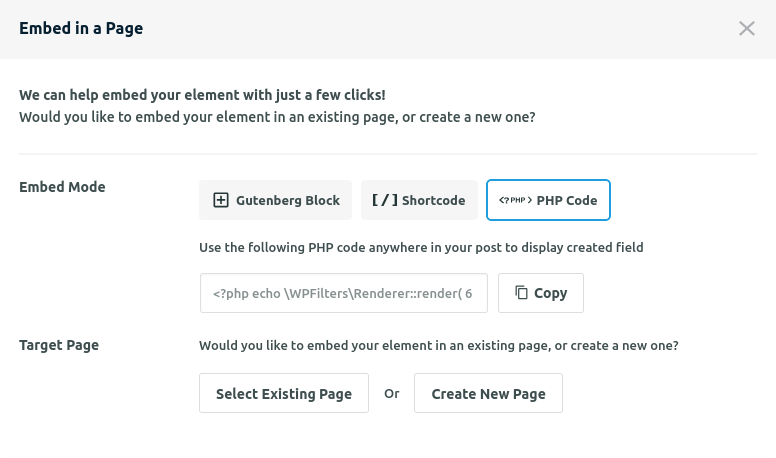
Gutenberg Block
The Gutenberg Block method provides the easiest way to add WPFilter Elements to your content using WordPress’s native block editor. While editing any page or post, search for the “WP Filter” block in the block inserter and add it to your desired location. From the block settings panel in the sidebar, select the appropriate filter element you wish to display. This method offers the most user-friendly approach and integrates seamlessly with WordPress’s editing experience.
Shortcode
Each filter element includes a unique shortcode that you can copy and paste into any page, post, or widget area. This method provides universal compatibility across different page builders and theme templates, making it ideal for users who need to add filters to various locations throughout their site without modifying theme files.
PHP Code
For developers working with custom theme files or advanced implementations, WPFilters provides a PHP code snippet for each element. This allows you to insert filter elements directly into theme template files or implement them through a code snippet plugin, providing maximum control over placement and integration with custom theme functionality.
Target Page Selection
WPFilters includes a convenient target page selector that allows you to add a filter block to an existing page directly from the Elements configuration screen. Alternatively, you can create a new page specifically for displaying the filter element, streamlining the process of setting up new filtered content displays on your site.
.