Wondering how to create a custom search in WordPress without a plugin?
By customizing search on your site, you can increase the number of pageviews, boost your sales, and help your visitors find what they came for faster.
In this article, we’ll talk about how you can customize search on your site without installing a plugin and why you should still consider using a plugin to do that.
Let’s begin!
Why is Custom Search Important to Your WordPress Website?
To get started, let’s talk about how a custom search on your site can help you grow your business.
Customizing search on your site allows you to:
- Deliver more relevant search results. Limit your search to specific categories to narrow your search results and help visitors find what they’re looking for faster.
- Get more pageviews and sales. Boost your content discoverability and increase your income by promoting specific posts or products in your search results.
- Build a loyal audience. Visitors who’ve had a positive search experience on your site are more likely to return again to explore more of your content.
- Drive more traffic from search engines. By helping visitors find the right content faster, you make them stay on your site longer, which is one of the main ranking factors in Google.
After we’ve figured out what benefits custom search can bring to your business, let’s talk about what disadvantages you can expect if you do that without a plugin.
Drawbacks of Creating Custom Search Without A Plugin
You should consider a couple of major drawbacks if you want to create a custom search on your site without a plugin.
1. It Requires Coding Skills and Deep WordPress Knowledge
The main disadvantage of customizing your site search manually is that it requires extensive coding experience and deep knowledge of WordPress.
The thing is, there are no default search configuration tools in WordPress.
Due to that, the only way to customize your search is to modify WordPress core files and the code of your theme.
It’s inconvenient, time-consuming, and unsuitable for non tech-savvy people.
Moreover, if you do something wrong, it can lead to the crash of your site, so you should be very careful when customizing your theme files.
2. You’ll Have Fewer Features
Plus, even if you have extensive coding skills, the number of custom search features you can add without a plugin is limited.
For example, you can’t add multiple search engines with a unique set of rules, exclude specific pages or categories from search, manage the order of your search results, and many more.
So if it’s crucial for you to get complete control over how search works on your site, you should consider using a powerful WordPress search plugin.
3. You May Lose Your Changes
Finally, since customizing search without a plugin requires making edits to your site’s files, you’ll lose all changes you made when you update your theme or WordPress version.
The best way to avoid such situations is to use a WordPress search plugin, as it keeps your settings whatever you do with your site.
With that, let’s take a look at how you can customize search on your site in a few clicks, with no coding needed and regardless of your technical skills.
Easiest Method for Customizing WordPress Search on Your Site
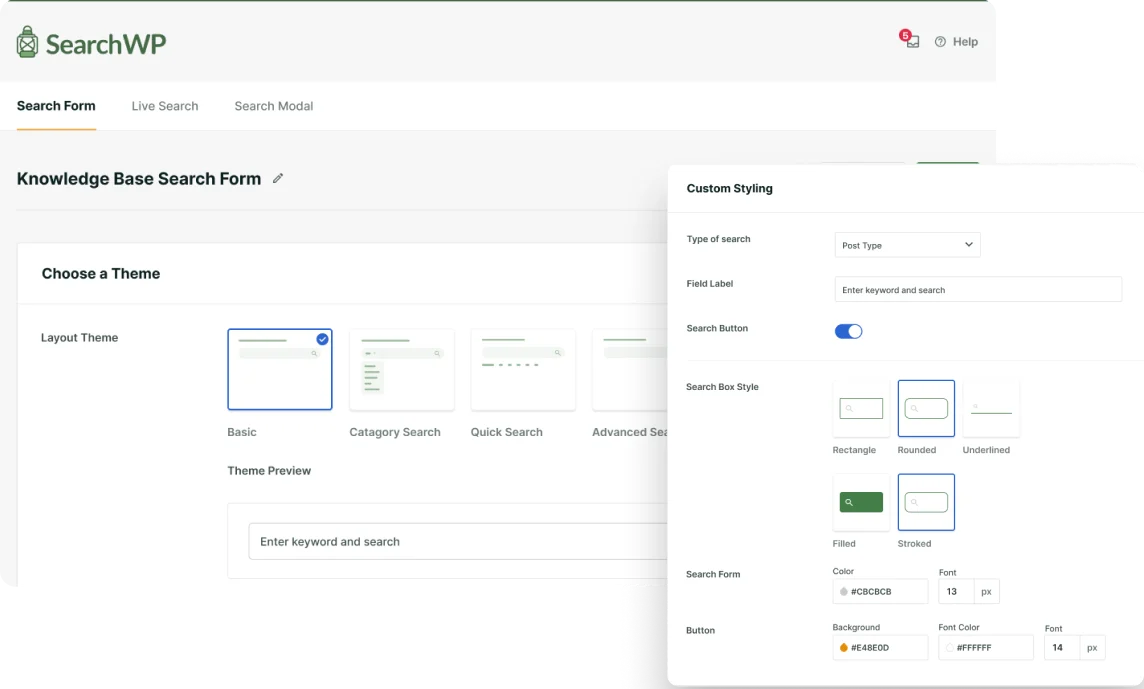
The easiest way to customize a search on your WordPress site is to use a plugin like SearchWP.
SearchWP is the top-rated WordPress search plugin trusted by over 50,000 website owners.
Its beginner-friendly interface and powerful features allow you to fully customize your search even if you launch your first website.
For example, with SearchWP, you can manage where WordPress should look for matches, limit search to a specific type of content, enable search by tags and custom fields, and many more.
The best thing is that you can do most of these things in just a few clicks.
You can also use SearchWP to:
- Show search results in live mode: Enable live display of search results on your site so your visitors can instantly navigate to the content they want.
- Track searches of your visitors: Collect data on what visitors are searching for on your site, which results are most clickable, and other valuable data.
- Highlight search terms in search results: Help your visitors figure out if they’ve found the right content faster by highlighting keywords in search results.
- Exclude specific pages from search: Get rid of clutter in search results on your site by excluding redundant pages and outdated content.
After you learn why SearchWP is the best WordPress search plugin, let’s see how you can use it to customize search on your site for your needs.
Step 1: Install and Activate SearchWP
The first step is to go to the SearchWP website and grab your copy of SearchWP.
Once done, simply go to your SearchWP account dashboard and click Downloads.
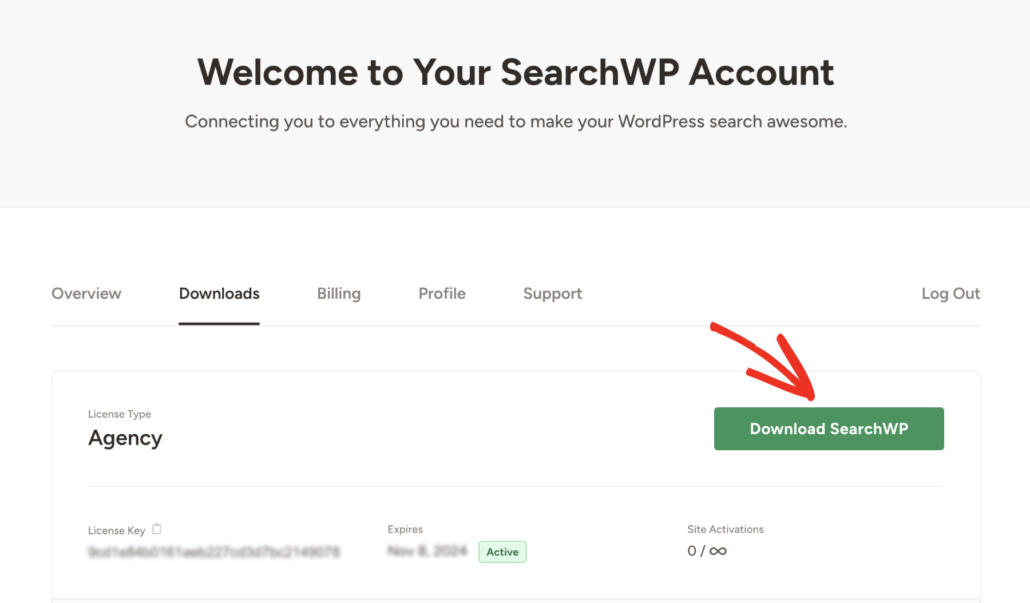
Then, you can press the Download SearchWP button and save the plugin to your computer.
After downloading, we also suggest to copy your SearchWP license key at the bottom left corner.
Next, you’ll need to install SearchWP on your site. If you need help, you can follow our detailed guide on installing a WordPress plugin.
After that, you will see the SearchWP welcome screen and setup wizard. Go ahead and click the ‘Start Onboarding Wizard’ button and follow the onscreen instructions.
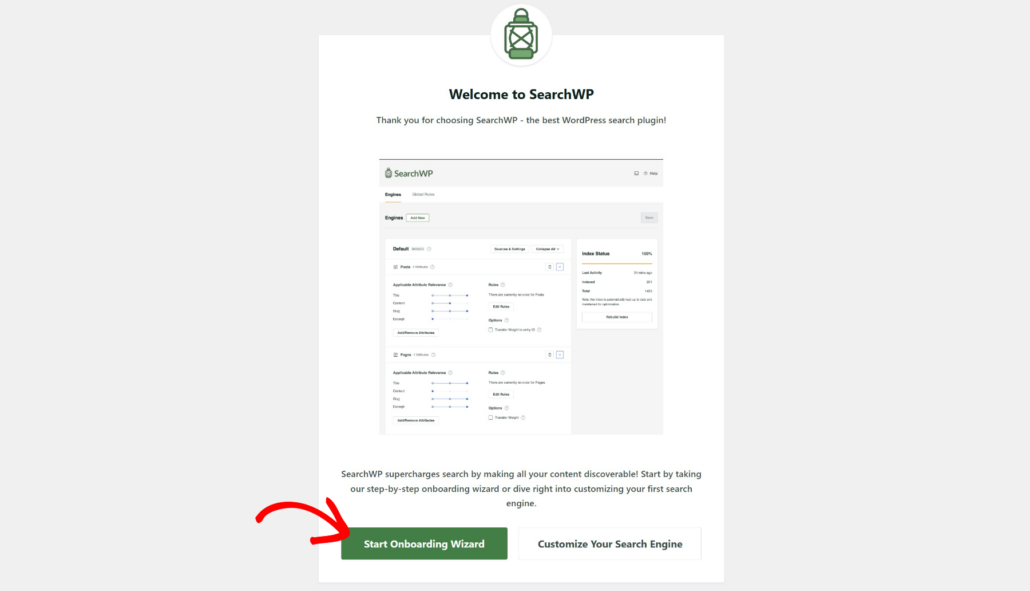
Step 2: Start Customizing Your Search
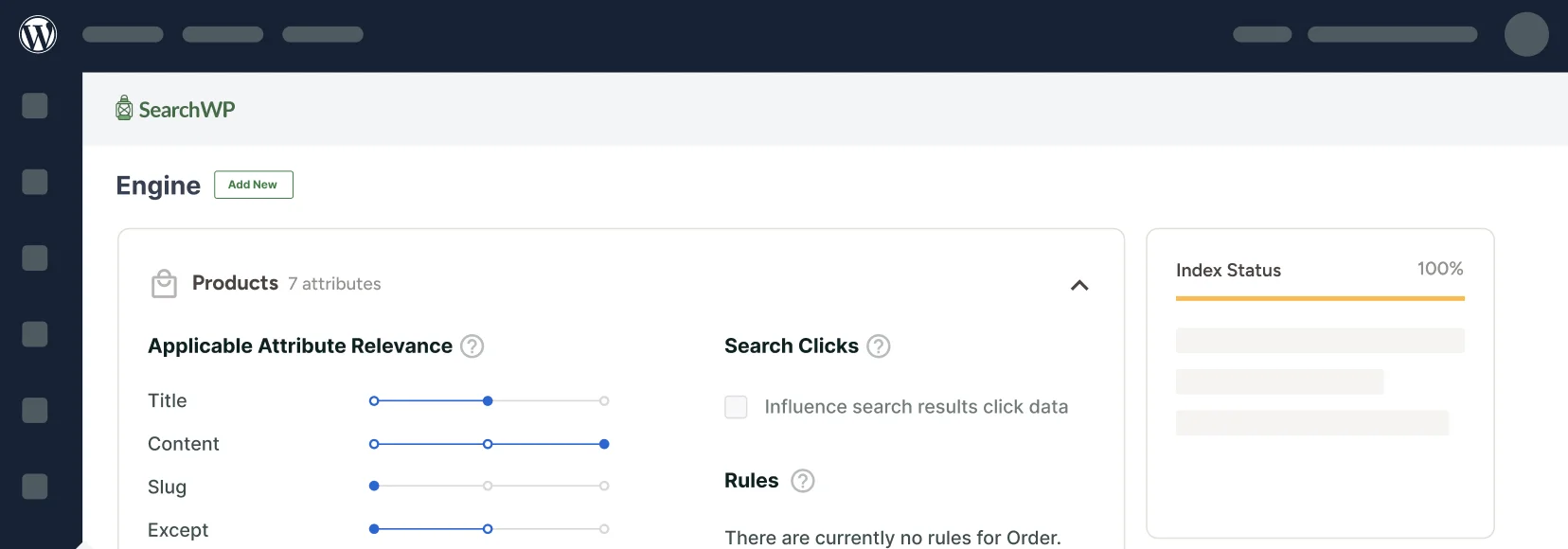
Next, you can add, remove and customize search engines in SearchWP. Think of them as set of rules that will be followed when performing a search on your site.
By customizing the engine, you can manage the list of your search sources, make it consider new content attributes, limit search to specific categories, and more.
With SearchWP, you can add an unlimited number of search engines and connect them to individual search forms on your site.
Thanks to that, you can quickly create custom search forms for various business needs and place them wherever you want on your site.
Since in this tutorial we want to customize how search works throughout the whole site, we’ll edit the Default search engine.
First, let’s specify where WordPress will search for content by configuring its list of search sources.
Manage Your Search Sources
To get started, head to SearchWP » Algorithm from your WordPress dashboard.
From here, you can press the Sources & Settings button.
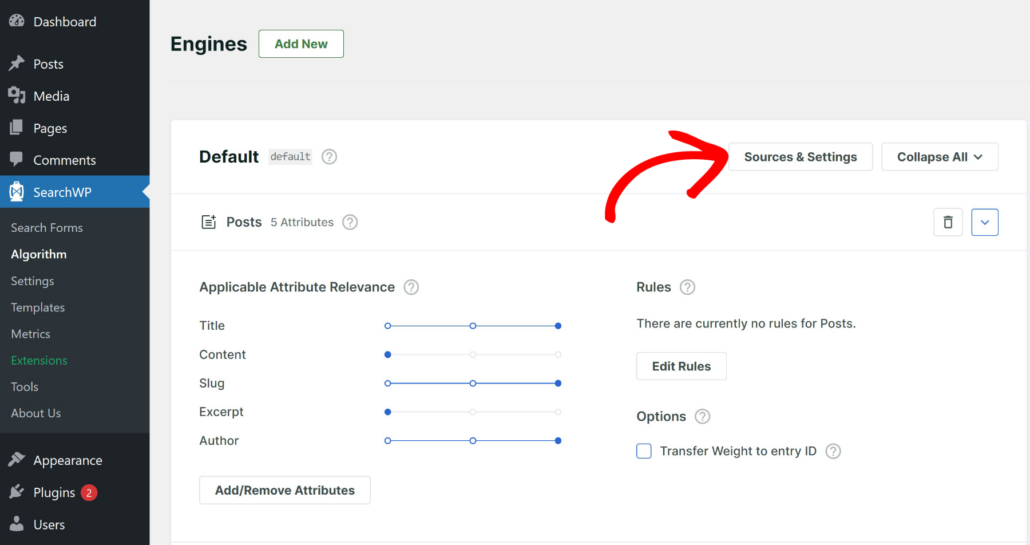
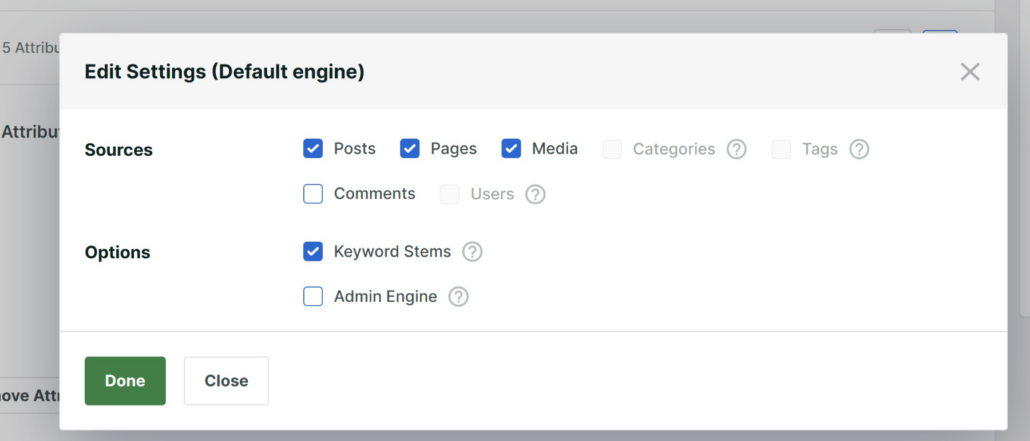
Here you can manage which sources to include in the search process.
By default, it searches among Posts, Pages, and Media files.
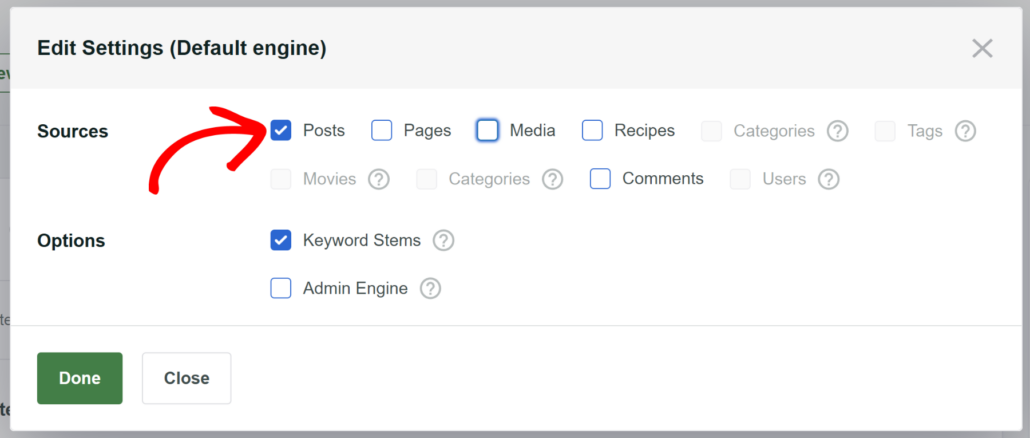
To remove a search source, you can uncheck a box next to it. For example, let’s limit search on our site to posts only.
To do that, we’ll uncheck all other sources except Posts and then click Done to save the changes.
Once we’ve set up our list of search sources, let’s also enhance our search by making WordPress consider post attributes and taxonomies.
Configure Your Search Attributes
To get started, you can click the Add/Remove Attributes button in the Posts search source section.
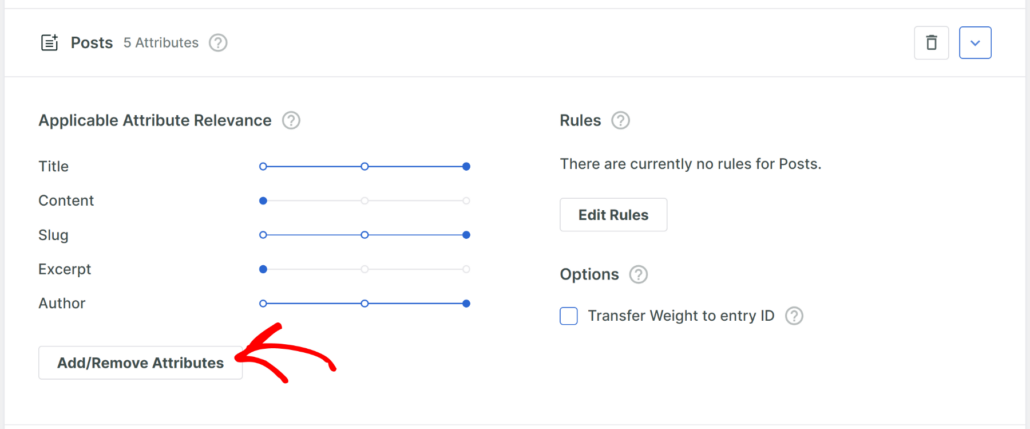
On the next window, you can specify attributes like custom fields and taxonomies you want SearchWP to consider when performing a search.
By default, it will include title, content, slug, excerpt, and author as attributes.
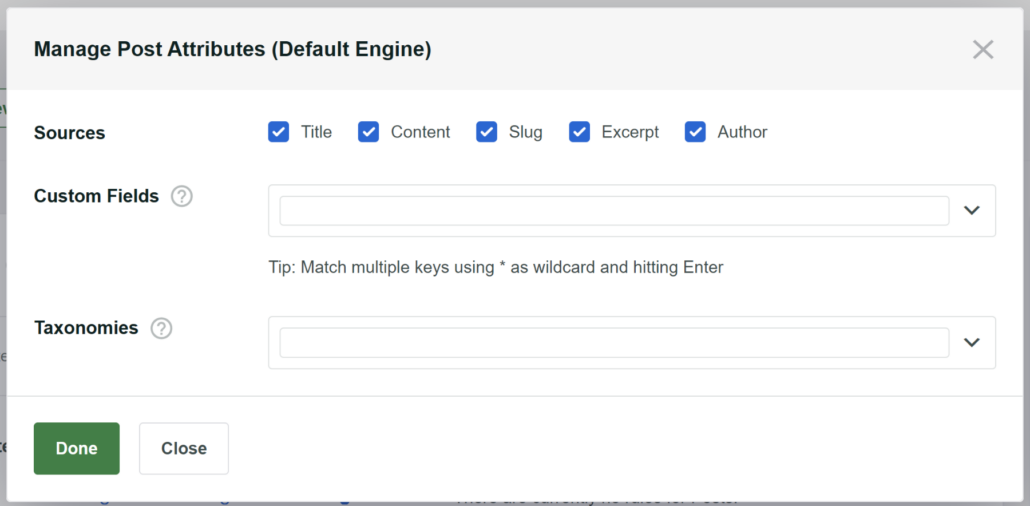
To make a specific custom field searchable, you can click on the Custom Fields field and enter its name.
Similarly, you can also include taxonomies like tags and categories for the source.
To make a new taxonomy searchable, click the Taxonomies field and select the desired taxonomy.
For instance, let’s make WordPress consider post tags when performing a search. To do that, choose the Tags option from the dropdown menu.
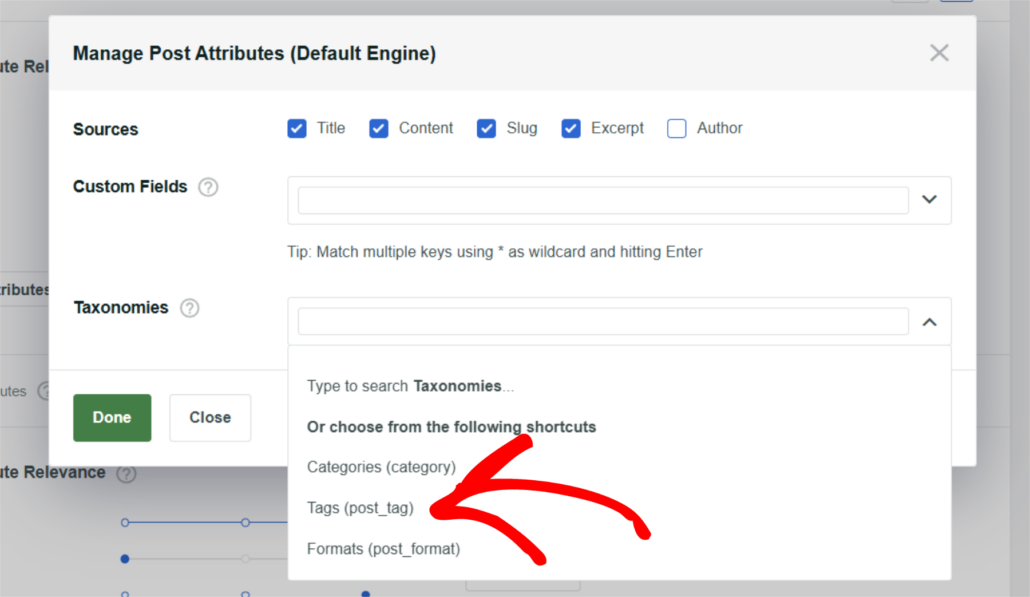
After you finish managing the Posts source attributes, press Done to save the changes.
Now, let’s see how you can narrow your search to give your visitors more relevant results.
Limit Search to a Specific Post Category
To get started, go ahead and press the Edit Rules button for your source.
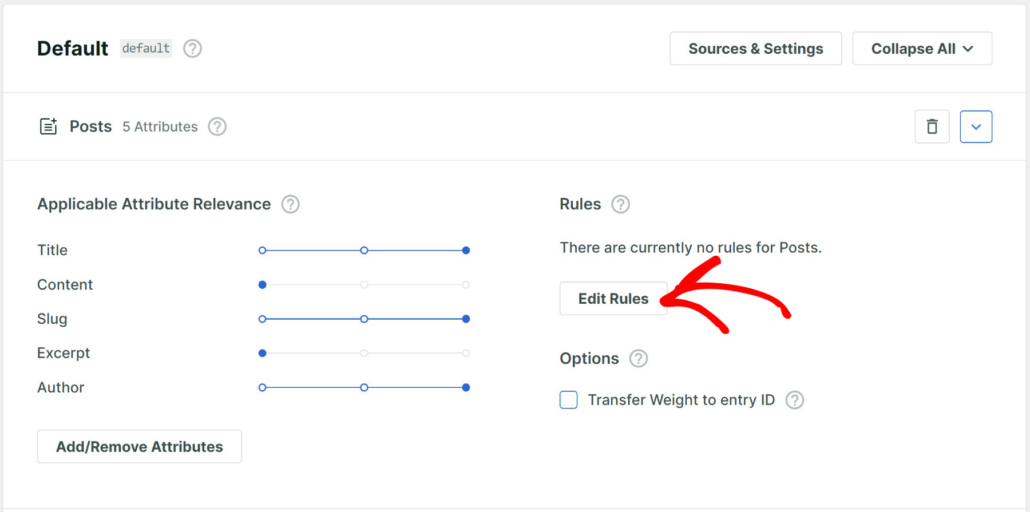
A new window will now popup.
Simply click the Add Rule button.
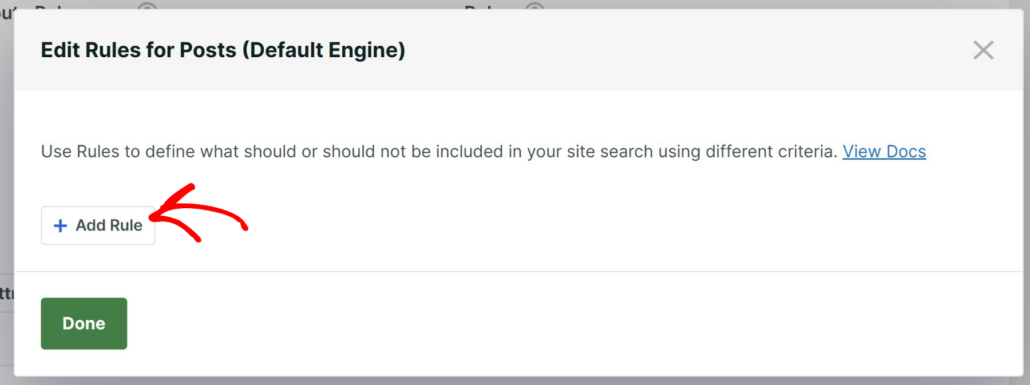
Here you can add rules according to which WordPress will filter content in search results.
For instance, you can add a rule to exclude specific categories from your search or limit your search to them.
Let’s assume we want to limit search on our test site to the News category.
To do that, first make sure you choose the Exclude entries if: option and then choose the Categories taxonomy.
From here, you can then enter the name of a category you want to limit your search to in the rightmost field. In our case, it’ll be the News.
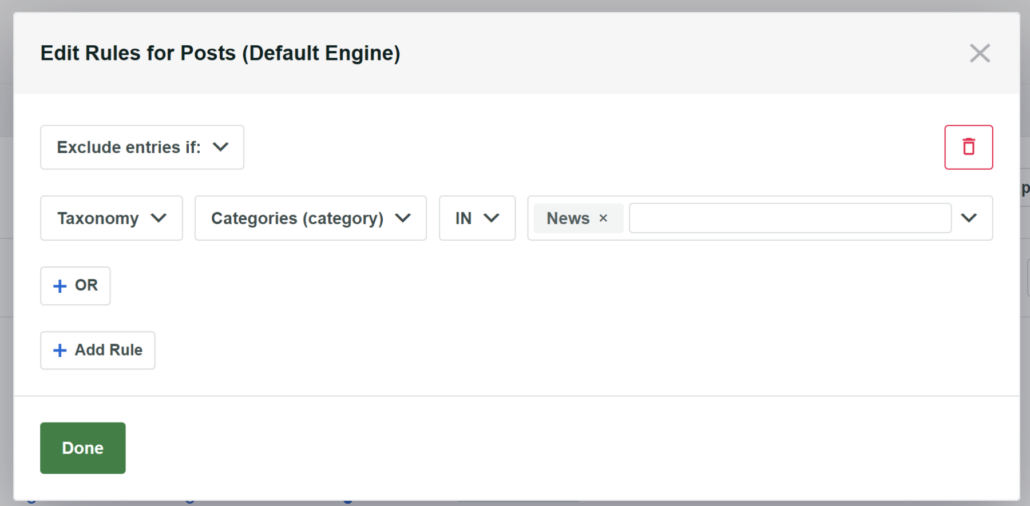
After you finish customizing the rules of your search engine, click Done to save your changes.
When you’re happy with how you customized your search, you’re ready to move to the final step and save your search engine.
Save Your Search Engine
To do that, go ahead and press the Save button at the upper right corner of your SearchWP dashboard.
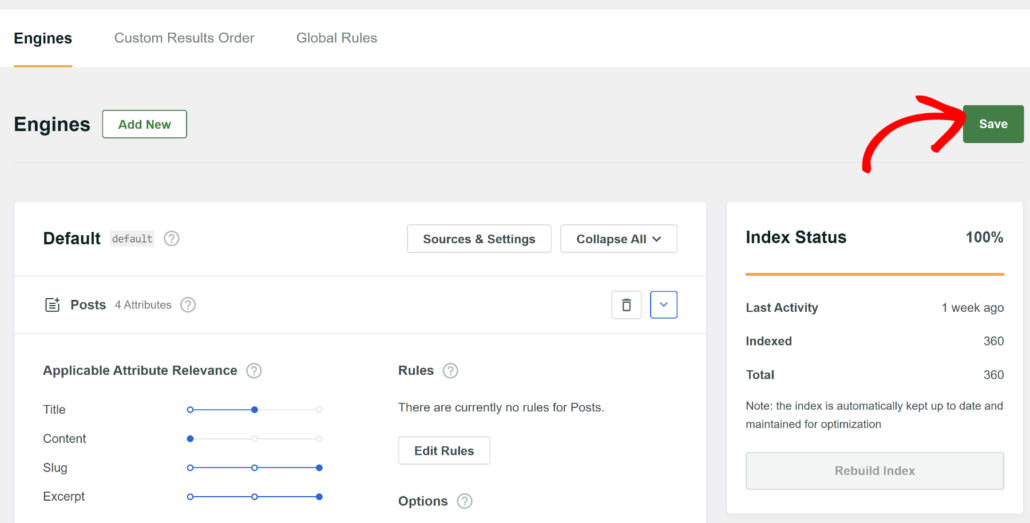
That’s it. You’ve fully customized search to your needs without writing a single line of code.
Let’s test your new search to make sure it works according to your customizations.
Step 3: Test Your New Search
To get started, go to your website and perform a test search.
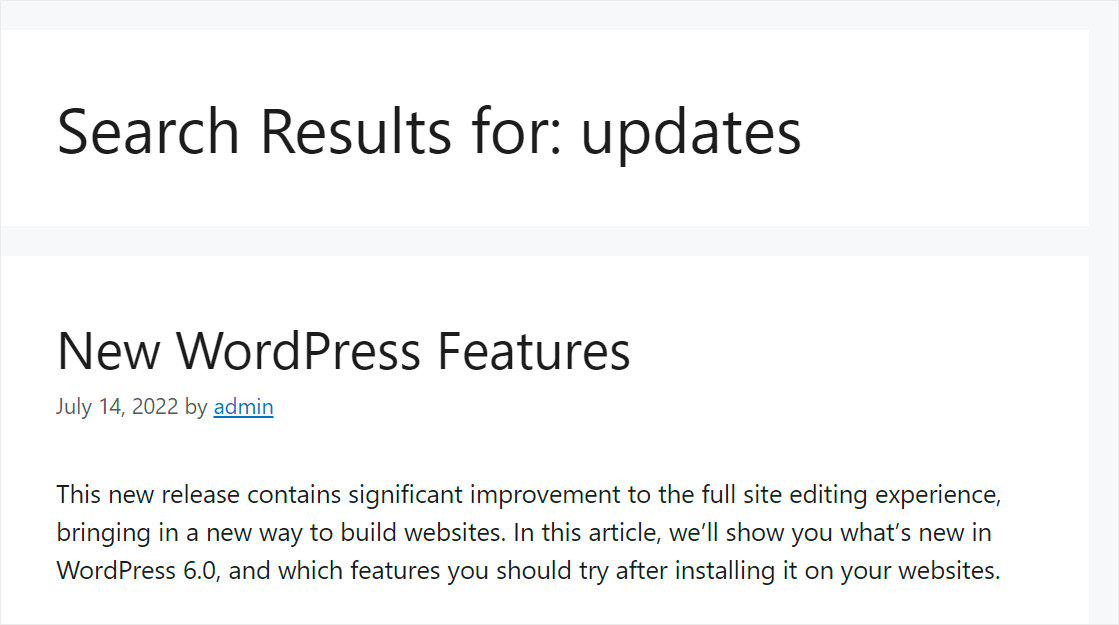
For example, since we made post tags searchable, let’s try to find a post by its tags only.
On our test site, we have a post called “New WordPress Features”, which has the “Updates” tag.
Let’s search by this tag and see if we can find our post.
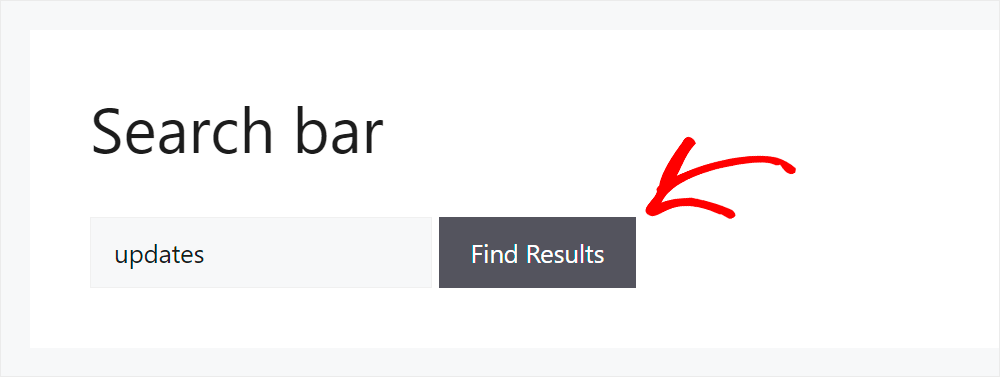
We found the post even though there is no word “updates” in its title, excerpt, or content.
It means that our search engine now considers post tags when looking for matches.
Let’s also make sure that search on our site is now limited to the “News” category.
To do that, we’ll search for “WordPress”, since we have many posts related to WordPress in other categories.
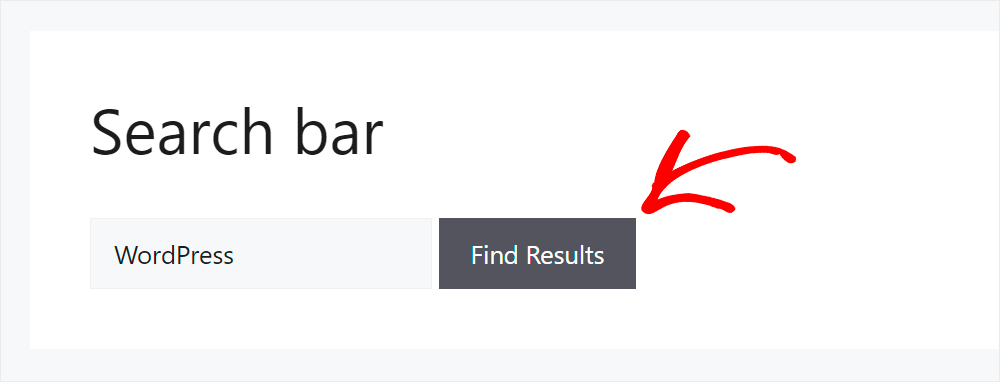
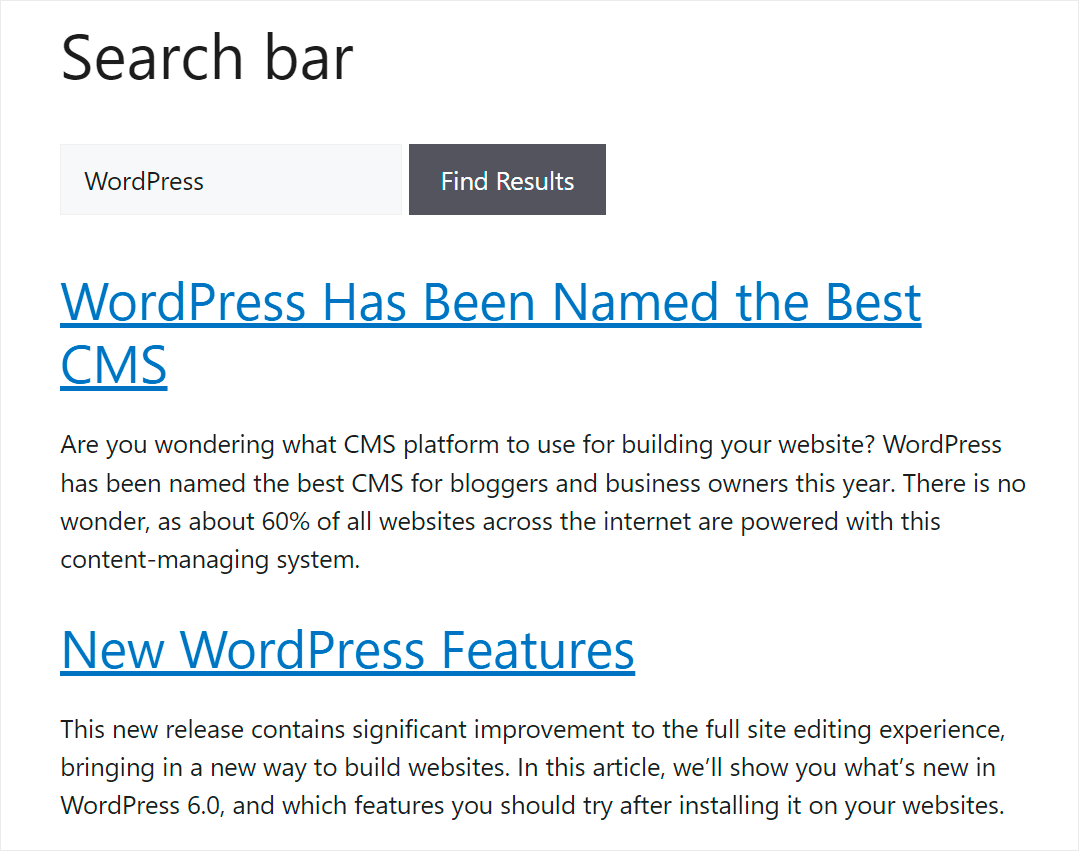
You can see that only posts from the News category are displayed among the search results that we got.
It means that the rule we added to our search engine, which says that WordPress should only search among the news, works as it should.
So, you’ve just learned the easiest way to customize your search. Now let’s see how you can do it without using a plugin.
Create Custom Search in WordPress Without a Plugin
To customize your search without a plugin, you’ll need to make edits to your theme.
The safest way to do that is to create a child theme of the current theme you’re using on your site.
This way, when you make changes to a child theme, your parent theme remains untouched, allowing you to quickly switch to it in case of critical errors.
Plus, having a child theme allows you to update your parent theme without losing your changes. For more details on how to create a child theme, check out this how to create a child theme tutorial.
Pro Tip: You can also use a WordPress backup plugin to make sure you have a fresh copy of your site ready to restore in case something goes wrong.
After you create and activate a child theme, you’re ready to start customizing your search.
To get started, navigate to Appearance » Theme Files Editor in your WordPress dashboard. Then, find the functions.php file on the right panel and click on it.
If you’re not comfortable editing the theme files, then we suggest using WPCode. It helps you insert custom code to your site without risking breaking anything. You can go through this guide on how to copy and paste code snippets from the web into WordPress.
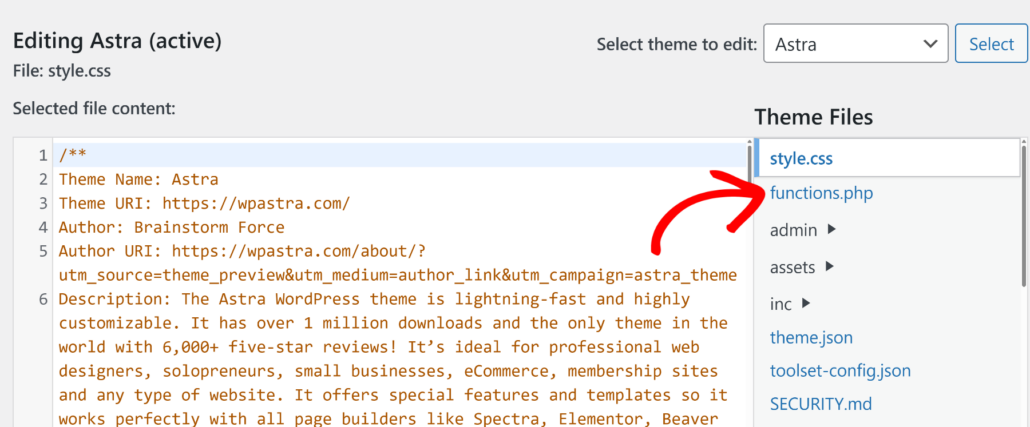
After that, follow the instructions below depending on what customizations you want to make to search on your site.
Enable Search Posts by Tags and Categories
To make post tags and categories searchable on your site without a plugin, you’ll need to add the following code to your theme’s functions.php file.
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*
* Search Posts by Tags and Categories
*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*/
/**
* Join the terms, term_relationship, and term_taxonomy tables.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $join The JOIN clause.
* @param object $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The JOIN clause.
*/
function search_custom_posts_join( $join, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $join;
}
$join .= &amp;amp;quot;
LEFT JOIN
(
{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_relationships}
INNER JOIN
{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_taxonomy} ON {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_taxonomy}.term_taxonomy_id = {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_relationships}.term_taxonomy_id
INNER JOIN
{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;terms} ON {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;terms}.term_id = {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_taxonomy}.term_id
)
ON {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts}.ID = {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_relationships}.object_id &amp;amp;quot;;
return $join;
}
add_filter( 'posts_join', 'search_custom_posts_join', 10, 2 );
/**
* Modify the WHERE clause to include searches against taxonomies.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $where The WHERE clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The WHERE clause.
*/
function search_custom_posts_where( $where, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $where;
}
// Get additional where clause for the user.
$user_where = '';
$user_id = get_current_user_id();
$status = array( &amp;amp;quot;'publish'&amp;amp;quot; );
// Include private posts if the user is logged in.
if ( $user_id ) {
$status[] = &amp;amp;quot;'private'&amp;amp;quot;;
$user_where .= &amp;amp;quot; AND {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts}.post_author = {$user_id}&amp;amp;quot;;
}
$user_where .= &amp;amp;quot; AND {$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts}.post_status IN( &amp;amp;quot; . implode( ',', $status ) . &amp;amp;quot; ) &amp;amp;quot;;
$where .= &amp;amp;quot; OR (
{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;term_taxonomy}.taxonomy IN( 'category', 'post_tag' )
AND
{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;terms}.name LIKE '%&amp;amp;quot; . esc_sql( get_query_var( 's' ) ) . &amp;amp;quot;%'
{$user_where}
)&amp;amp;quot;;
return $where;
}
add_filter( 'posts_where', 'search_custom_posts_where', 10, 2 );
/**
* Set the GROUP BY clause to post IDs.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $groupby The GROUPBY clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The GROUPBY clause.
*/
function search_custom_posts_groupby( $groupby, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $groupby;
}
return &amp;amp;quot;{$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts}.ID&amp;amp;quot;;
}
add_filter( 'posts_groupby', 'search_custom_posts_groupby', 10, 2 );
</pre>
When you’re finished, press the Update File button to save your changes.
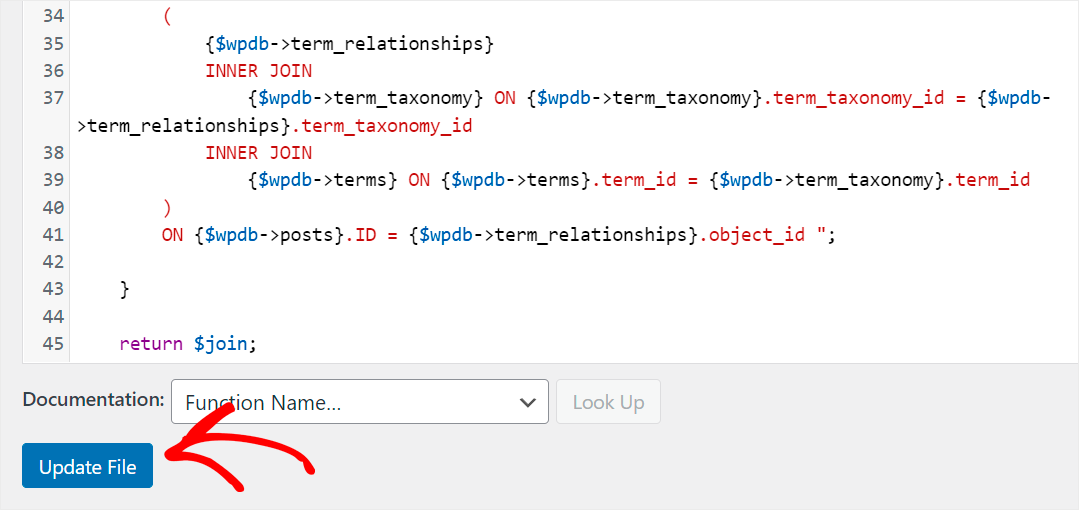
Now your site visitors can search for posts by tags and categories.
Enable Search by Comment Content and Author Names
To make comments and author names searchable on your site without a plugin, add the following code to your theme’s functions.php file:
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*
* Search by Comment Content and Author Names
*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*/
/**
* Joins the comments and posts tables.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $join The JOIN clause.
* @param object $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The JOIN clause.
*/
function search_custom_comments_posts_join( $join, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $join;
}
$join .= ' LEFT JOIN ' . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;comments . ' ON ' . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . '.ID = ' . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;comments . '.comment_post_ID ';
return $join;
}
add_filter( 'posts_join', 'search_custom_comments_posts_join', 10, 2 );
/**
* Modify the WHERE clause to include searches against comments.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $where The WHERE clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The WHERE clause.
*/
function search_custom_comments_posts_where( $where, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $where;
}
$where = preg_replace(
&amp;amp;quot;/\(\s*&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . &amp;amp;quot;.post_title\s+LIKE\s*(\'[^\']+\')\s*\)/&amp;amp;quot;,
&amp;amp;quot;(&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . &amp;amp;quot;.post_title LIKE $1) OR (&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;comments . &amp;amp;quot;.comment_author LIKE $1) OR (&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;comments . &amp;amp;quot;.comment_content LIKE $1)&amp;amp;quot;,
$where
);
return $where;
}
add_filter( 'posts_where', 'search_custom_comments_posts_where', 10, 2 );
/**
* Prevent search results duplicates.
*
* @param string $distinct The DISTINCT clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The DISTINCT clause.
*/
function search_custom_comments_posts_distinct( $distinct, $query ) {
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $distinct;
}
return 'DISTINCT';
}
add_filter( 'posts_distinct', 'search_custom_comments_posts_distinct', 10, 2 );
When you’re done, click the Update File button at the bottom of the editor to save your changes.
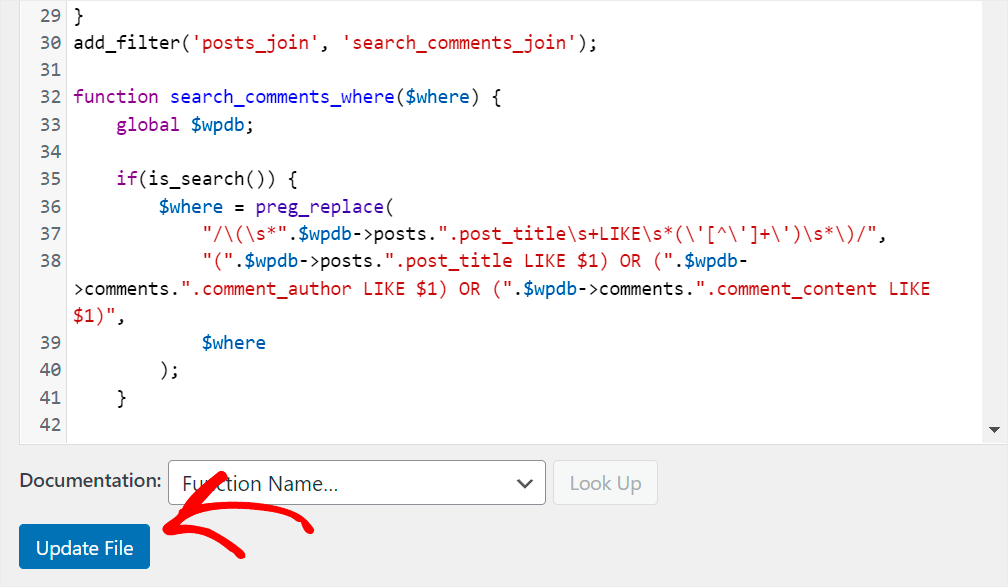
Now your visitors can search by comment content and author names.
Enable Search by Post Custom Fields
To make custom fields searchable on your site without a plugin, add the following code to your theme’s functions.php file:
<pre class="wp-block-syntaxhighlighter-code">
/*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*
* Search by Post Custom Fields
*
* ----------------------------------------------------------
*/
/**
* Joins the postmeta and posts tables.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $join The JOIN clause.
* @param object $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The JOIN clause.
*/
function search_custom_meta_posts_join( $join, $query ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $join;
}
$join .=' LEFT JOIN '.$wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;postmeta. ' ON '. $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . '.ID = ' . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;postmeta . '.post_id ';
return $join;
}
add_filter( 'posts_join', 'search_custom_meta_posts_join', 10, 2 );
/**
* Modify the WHERE clause to include searches against postmeta.
*
* @global $wpdb
*
* @param string $where The WHERE clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The WHERE clause.
*/
function search_custom_meta_posts_where( $where ) {
global $wpdb;
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $where;
}
$where = preg_replace(
&amp;amp;quot;/\(\s*&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . &amp;amp;quot;.post_title\s+LIKE\s*(\'[^\']+\')\s*\)/&amp;amp;quot;,
&amp;amp;quot;(&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;posts . &amp;amp;quot;.post_title LIKE $1) OR (&amp;amp;quot; . $wpdb-&amp;amp;gt;postmeta . &amp;amp;quot;.meta_value LIKE $1)&amp;amp;quot;, $where );
return $where;
}
add_filter( 'posts_where', 'search_custom_meta_posts_where', 10, 2 );
/**
* Prevent search results duplicates.
*
* @param string $distinct The DISTINCT clause.
* @param WP_Query $query The current WP_Query instance.
*
* @return string The DISTINCT clause.
*/
function search_custom_meta_posts_distinct( $distinct, $query ) {
if ( ! is_main_query() || ! is_search() ) {
return $distinct;
}
return 'DISTINCT';
}
add_filter( 'posts_distinct', 'search_custom_meta_posts_distinct', 10, 2 );
</pre>
Once done, press the Update File button at the bottom of the editor to save your changes.
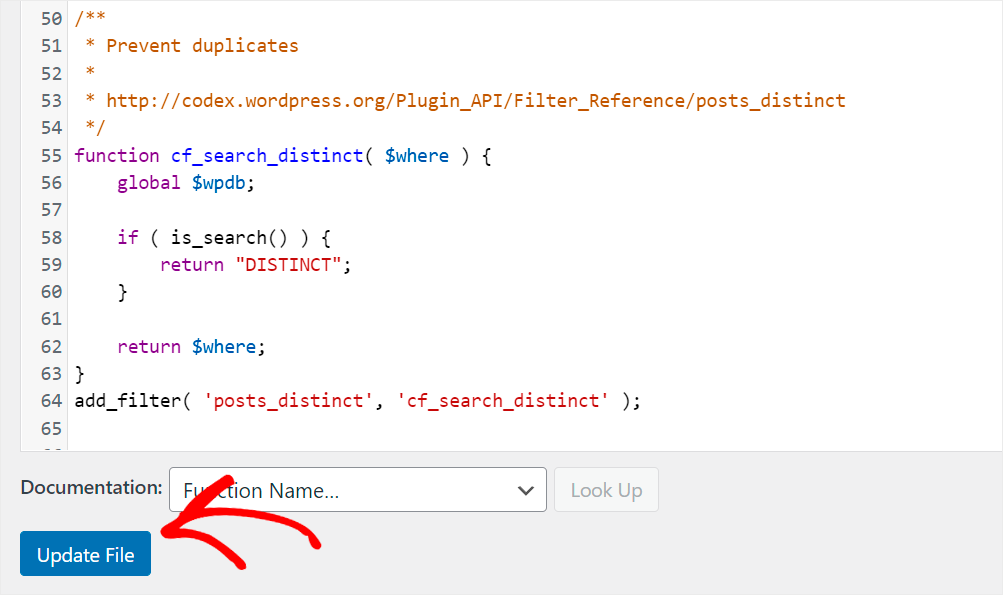
Now your visitors can search for posts by custom fields.
We hope this article helped you learn how to create a custom search on your site without a plugin. You may also want to see our guide on how to create a custom WordPress theme and how to customize your WordPress search results page.
Ready to customize search on your site in a few clicks? You can get started with SearchWP here.